
INCOME TAX RETURN
INTRODUCTION
The process of filing Income Tax Returns (ITR) is an annual exercise that every taxpayer in India is required to undertake. The Income Tax Return for Assessment Year (A.Y.) 2024-25, corresponding to the Financial Year (F.Y.) 2023-24, involves reporting income earned during this period and paying any tax due. This practice not only ensures compliance with tax laws but also aids in the financial planning and transparency of individuals and businesses.
CATEGORIES OF INCOME TAXPAYERS
The Indian Income Tax Act classifies taxpayers into several categories:
1. INDIVIDUALS: This category includes residents, non-residents, senior citizens (aged 60-80 years), and super senior citizens (aged 80 years and above).
2. HINDU UNDIVIDED FAMILIES (HUFS): Joint families as recognized under Hindu law.
3. COMPANIES: Domestic and foreign companies operating in India.
4. FIRMS: Partnership firms, including LLPs (Limited Liability Partnerships).
5. ASSOCIATION OF PERSONS (AOP) AND BODY OF INDIVIDUALS (BOI): Groups of individuals or entities who come together for a common purpose.
6. TRUSTS: Entities established for charitable or religious purposes.
7. ARTIFICIAL JURIDICAL PERSONS: Entities not covered under the above categories but deemed taxable by law.

TYPES OF INCOME TAX RETURNS
The Income Tax Department provides several ITR forms, each catering to different types of taxpayers and their specific income sources:
1. ITR-1 (SAHAJ): For individuals with income up to ₹50 lakh from salary, one house property, and other sources (excluding lottery winnings and income from racehorses).
2. ITR-2: For individuals and HUFs not having income from business or profession.
3. ITR-3: For individuals and HUFs having income from a proprietary business or profession.
4. ITR-4 (SUGAM): For individuals, HUFs, and firms (other than LLPs) having a total income up to ₹50 lakh and income from business and profession computed under sections 44AD, 44ADA, or 44AE.
5. ITR-5: For persons other than individuals, HUFs, companies, and those filing ITR-7.
6. ITR-6: For companies other than those claiming exemption under section 11.
7. ITR-7: For persons including companies required to furnish returns under sections 139(4A), 139(4B), 139(4C), or 139(4D).

KEY CHANGES AND UPDATES FOR A.Y. 2024-25
Several updates and changes have been introduced in the tax laws for A.Y. 2024-25:
1. INCOME TAX SLABS: The tax rates and slabs are reviewed periodically. For A.Y. 2024-25, the new tax regime introduced lower tax rates without deductions, while the old regime continued to offer deductions but at higher rates. Taxpayers have the option to choose between these regimes.
2. STANDARD DEDUCTION: Standard deduction for salaried individuals and pensioners remains available under the old regime.
3. SECTION 80C DEDUCTIONS: Investments in specified instruments like PPF, NSC, and life insurance premiums up to ₹1.5 lakh continue to be eligible for deductions.
4. DIGITAL PAYMENTS: Enhanced focus on digital transactions with incentives for digital payments to promote cashless transactions.
5. FACELESS ASSESSMENT AND APPEALS: Expansion of the faceless assessment and appeals process to reduce human interaction and improve transparency.
6. PRE-FILLED ITR FORMS: Introduction of pre-filled ITR forms to simplify the filing process. These forms will automatically capture details of income, TDS, and other information available with the Income Tax Department.
FILING PROCESS
The process of filing ITR involves several steps:
1. COLLECTING DOCUMENTS: Gather all necessary documents such as Form 16, salary slips, interest certificates, TDS certificates, and details of investments and expenditures eligible for deductions.
2. CHOOSING THE CORRECT ITR FORM: Select the appropriate ITR form based on your income sources and category.
3. FILING THE RETURN: Log in to the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal and fill in the required details in the chosen ITR form. You can also use third-party software or consult a tax professional.
4. VERIFICATION: After filing, verify your ITR using methods like Aadhaar OTP, EVC via bank account, or by sending a signed physical copy of ITR-V to the Centralized Processing Center (CPC) in Bengaluru.
5. PROCESSING OF RETURN: The Income Tax Department processes the verified returns and issues refunds if applicable.
DEDUCTIONS AND EXEMPTIONS
Various deductions and exemptions are available under the Income Tax Act, which taxpayers can use to reduce their taxable income:
1. SECTION 80C: Deductions up to ₹1.5 lakh for investments in PPF, NSC, ELSS, and payment of life insurance premiums.
2. SECTION 80D: Deductions for health insurance premiums paid for self, spouse, children, and parents.
3. SECTION 24(B): Deductions on home loan interest up to ₹2 lakh for a self-occupied property.
4. SECTION 80E: Deductions on interest paid on education loans.
5. SECTION 80G: Deductions for donations to specified charitable institutions and funds.
PENALTIES FOR NON-COMPLIANCE
Failure to file the ITR on time can attract penalties:
1. LATE FILING FEE: Under Section 234F, a late fee of ₹5,000 is applicable if the return is filed after the due date but before December 31 of the assessment year. Beyond this date, the fee increases to ₹10,000. For taxpayers with income up to ₹5 lakh, the late fee is restricted to ₹1,000.
2. INTEREST ON LATE PAYMENT: Interest under Section 234A, 234B, and 234C is levied for delay in filing and payment of taxes.
3. PROSECUTION: In cases of willful evasion, the Income Tax Department may initiate prosecution proceedings.
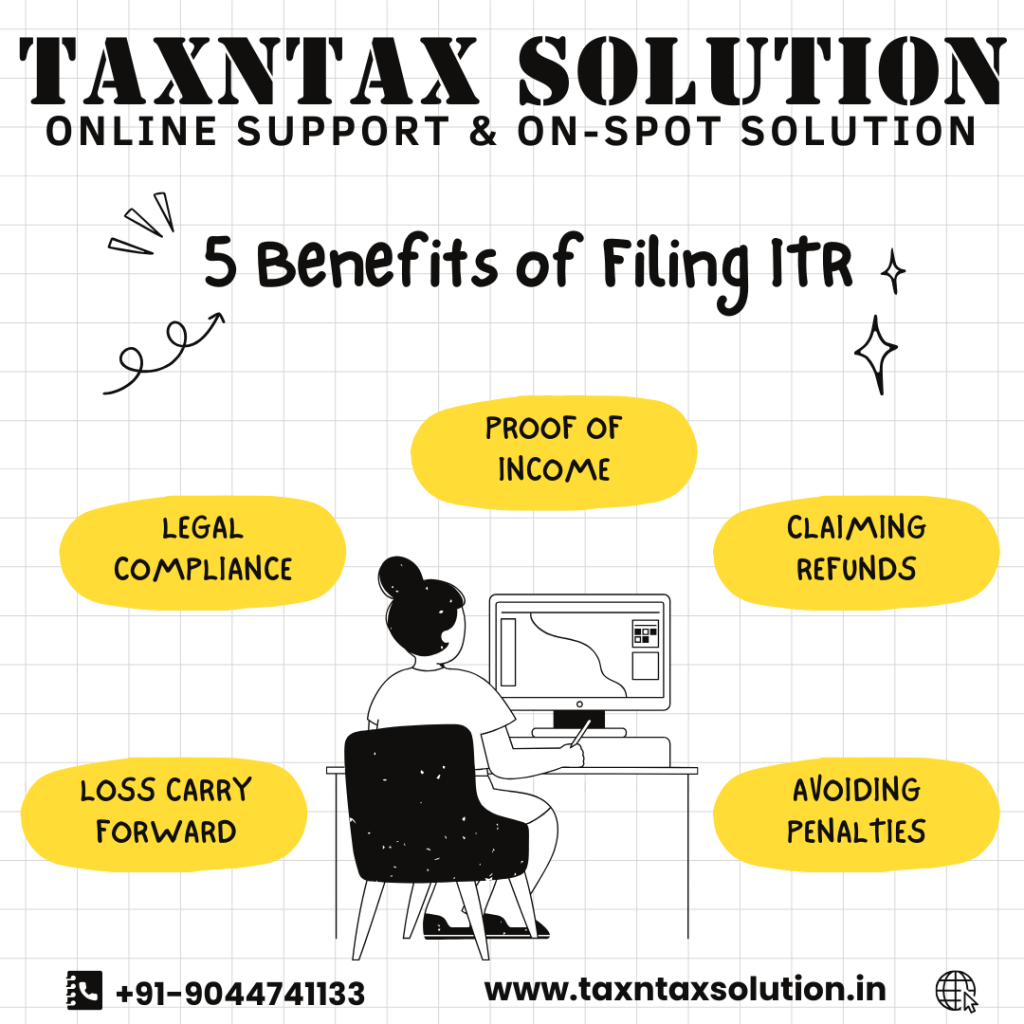
BENEFITS OF FILING ITR
1. LEGAL COMPLIANCE: Filing ITR is a legal obligation and ensures compliance with tax laws.
2. PROOF OF INCOME: ITR serves as proof of income for various purposes like applying for loans and visas.
3. CLAIMING REFUNDS: Filing returns is essential to claim refunds of excess tax deducted.
4. LOSS CARRY FORWARD: Losses incurred can be carried forward to subsequent years for set-off against future income, provided the return is filed on time.
5. AVOIDING PENALTIES: Timely filing helps avoid penalties and interest.
Filing Income Tax Returns for A.Y. 2024-25 is an important responsibility for taxpayers in India. With continuous updates and improvements in the tax system, including digital advancements and simplified processes, the task of filing returns has become more streamlined. Taxpayers should ensure they file their returns accurately and timely to avail of benefits, maintain compliance, and contribute to the nation’s development. The Income Tax Department’s focus on enhancing taxpayer experience through pre-filled forms, faceless assessments, and other initiatives is aimed at making the tax filing process as efficient and user-friendly as possible.
